School Facilities Belong in the Nation's Infrastructure Portfolio
- By Mary Filardo, Jeff Vincent
- 05/01/17
The American Society of Civil Engineers (ASCE) recently issued its 2017 report card rating 16 different categories of infrastructure. ASCE includes public school facilities in their infrastructure rating — grading them a D+1. However, state and federal plans to rebuild and modernize America’s infrastructure, often omit schools from our nation’s infrastructure portfolio.2
Public school buildings and grounds need to be fully included in state and federal planning and funding for the nation’s infrastructure.
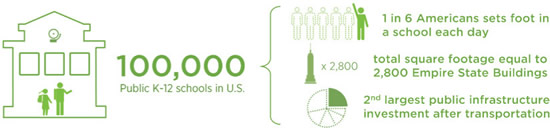
First, just like other major water, transit or port infrastructure, school facilities projects require long range planning and forecasting to ensure efficient use of land and other resources. Our nation’s public schools are estimated to be, on average, 44 years old and are multi-purpose facilities in our communities.3 They are shelters in case of emergencies or disasters, civic centers for voting and public meetings, community hubs for social activities and green space for parks and recreation. The quality and character of public school facilities affects the larger community over generations. Comprehensive and joint state, regional and municipal planning is critical to environmental and fiscal sustainability across public infrastructure assets.
Second, public school infrastructure, is financed through bonds repaid over many years. Public school construction, like water treatment plants and other infrastructure with multi-generational use, employs capital financing to pay for design, construction and major improvements. This financing of capital requires complex policy and finance associated with securing debt, and the need for adequate revenue streams for repayment. Local school districts alone had $409 billion of long-term debt at the end of fiscal year 2014.4 School construction is a close second to highways in average annual capital outlay for state and local expenditures.5
Third, like nearly all public works projects, the nearly $50 billion a year for school district capital outlay is delivered by the private for-profit building industry. The management and delivery of school construction and building improvements are done under the authority of public commissions, boards and administrators, but the work is delivered through contracts with private companies. School districts share with their counterparts in water, transportation, utilities and other sectors the need to manage private industry expertise, services and interests from the public interest.
But perhaps most important, is that public education is mission critical to the health, safety and prosperity of our nation. The transfer of knowledge from one generation to another through our public educational system is an essential personal AND public responsibility. The United States has developed a remarkable physical infrastructure — of school buildings and grounds that both delivers education and keeps our children engaged and safe while their parents and guardians work.
It is beyond time for our leaders in K-12 public school facilities to be at the “transportation and infrastructure” table. State and local public school facilities officials need to be in all state and federal discussions about rebuilding the nation’s infrastructure.
1 www.infrastructurereportcard.org, American Society of Civil Engineers, 2017.
2 See Priority List: Emergency and National Security Projects from Trump Elect, and February 8, 2017, LA Times article: California submits a $100-billion wish list of infrastructure projects to Trump for federal funding.
3 U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics, Fast Response Survey System (FRSS), “Condition of Public School Facilities: 2012–13,” FRSS 105, 2013.
4 National Center for Education Statistics, Fiscal Data, file: elsec14.xls, released 6/9/16.
5 State of our Schools, 2016, from U.S. Census of Governments, F-13 data.
This article originally appeared in the issue of .
About the Authors
Mary Filardo, Executive Director of the 21st Century School Fund.
Jeff Vincent, PhD., is deputy director and co-founder of the Center for Cities + Schools at the University of California-Berkeley.