Reinventing the Academic Workplace
A look at spaces that shape student-faculty interactions on campus, and ultimately contribute to student success.
- By Amy Hoffman, Shawn Gaither
- 07/16/19
Student demographics are constantly evolving and transforming as new generations step onto college campuses for the first time. With each new cohort comes a different set of expectations for the physical learning environment, as well as the interactions they anticipate they’ll have with faculty members. Faculty offices, both locale and layout, factor into the ability for students and professors to establish meaningful relationships that help students navigate their collegiate years and beyond. Therefore, we pose the question: How does the design of faculty and administration spaces contribute to student success?
To answer this question, we need a baseline definition of today’s students and why they would rely more heavily on faculty engagement than previous generations.
Let’s put this evolving demographic into perspective: according to Success by Design: Improving Outcomes in American Higher Education via Deloitte, more than 44 percent of today’s students are over the age of 24, 30 percent are considered part-time students, 28 percent are taking care of children or dependents, and 26 percent work full-time while enrolled. These figures are indicative of a new student population that may not always be able to schedule their days around traditional office hours, but rather rely on serendipitous interaction with their faculty members before and after classes.
Shifts in student population are compelling institutions to rethink what a campus faculty and administrative workplace should look like, placing greater emphasis on ease of accessibility, viability, and flexibility that supports open collaboration and relationship building. There is a trending connection between how and where faculty workspaces take shape on campus, and the impact they have on student success. A Gallup-Purdue University study found graduates with engaged professors were two times more likely to be engaged in life and work after graduation, but fewer than 14 percent of graduates reported having this experience with their faculty.
These statistics tell a provocative story—one that can be interpreted as an urgent need to change the way faculty offices are designed within a campus environment. But institutions, especially those that have been in existence for centuries and are steeped in history, often ask questions like, “how do we transform the traditional faculty office into a student-centric environment?” and “what do those new-founded environments look like?”
To answer those questions, we’ve identified three concepts that are centered around collaboration to enhance connections. All concepts ideally contain places for research, private conversations, and group work. 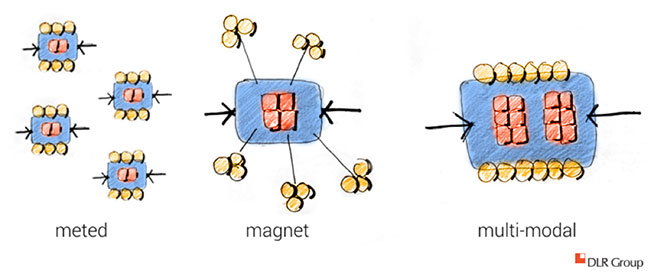
- The meted concept, or distributed “mini-suites,” is achieved by disbanding a group of faculty offices from one separate building and dispersing them throughout the campus where students spend the majority of their day.
- The magnet creates a “third place” with a central hub for student interaction, either one-on-one or in small groups. Private meeting space for faculty and students, as well as collaboration areas, are designed in clusters and located closer to labs and classrooms, giving students direct access from their learning environment. Faculty research is done elsewhere and is aligned spatially with ‘heads down” tasks.
- The multi-modal concept elevates community and entrepreneurial spirit to a new level. This one-stop concept can be located almost anywhere on campus, with the idea that it houses all aspects of a student-faculty experience. Its purpose is to be open and transparent and contains fixed and flexible environments that allow for autonomous or collaborative activities.
Work Space Evolution
At the same time student needs are evolving, the built environment is also experiencing a dramatic transformation. As expectations for interior spaces are increasing, employers are seizing opportunities to amend their workspaces and are using the environment as a recruiting tool to attract the best and brightest talent.
Another factor is space itself. Universities are often drastically short on faculty office space. Consequently, the ability to assign the traditional 120-square-foot enclosed office to every faculty member is impossible on most campuses, and not the best utilization of the space.
To coincide with the three concepts introduced earlier, we’ve identified three spatial elements for the new academic workplace—variety, collaboration, and flexibility.
- The primary goal is to provide users with variety in the size and type of space they use to perform their daily tasks. Huddle spaces of various sizes with a plethora of furniture choices, writable surfaces, and easy hookups to screens allow teams to conference efficiently. Also, small phone rooms are beneficial for short calls or when the need for a few quiet moments arise.
- Collaborative spaces, such as break rooms, makerspaces, reception areas, and learning stairs are magnets, drawing people in to work together in open and active environments. One national trend that supports this open, shared environment is the reduction in the number of full-time tenured faculty and an increase in part-time or adjunct professors who are not typically assigned a dedicated office. According to the American Association of University Professors, full-time non-tenure track and part-time professors make up more than 57 percent of the academic labor force, while full-time tenured and tenure-track faculty equal less than 30 percent.
- Real estate is too expensive for space to have a single function. Flexibility can be achieved in multiple ways; through physical changes like mobile walls and roll-up doors on multi-use spaces like a training room, or large conference rooms that allow adjacent spaces to morph and accommodate various groups and their needs. In addition, flexibility is achieved through the sharing of spaces.
Reinventing the academic workplace is a bold move, but one that could positively contribute to student success by creating spaces that encourage and advance meaningful student-faculty interactions.